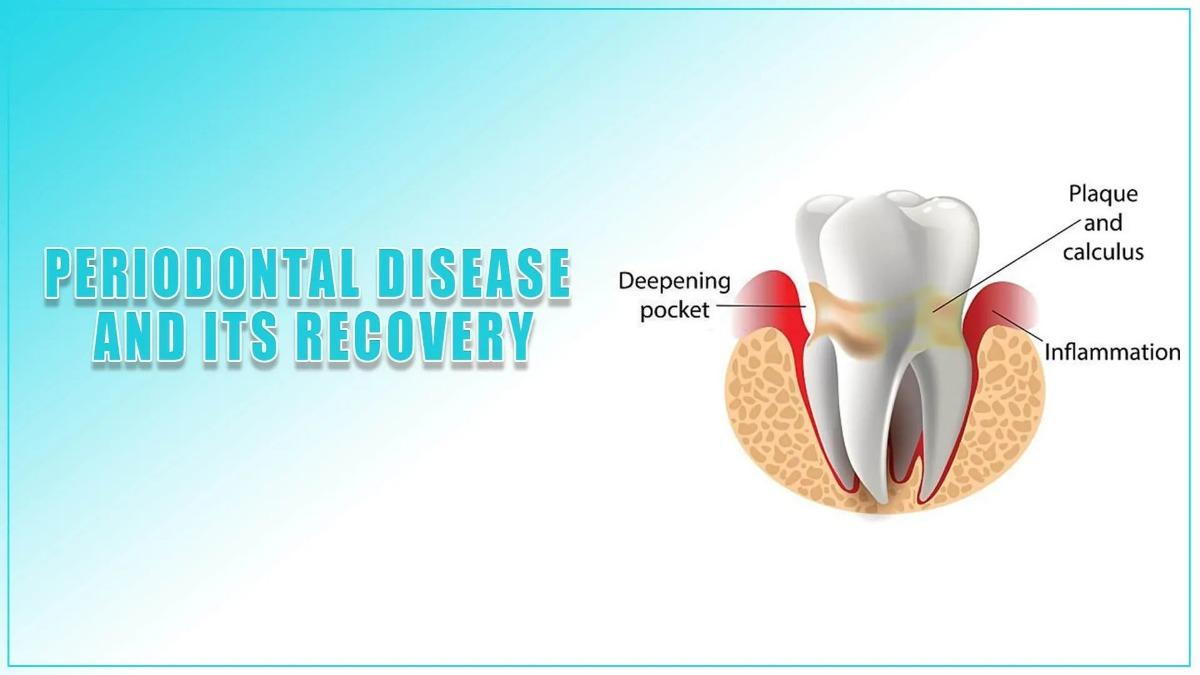
Periodontal disease is chronic gum disease. Periodontal disease develops once plaque has raised and hardened. They are usually a result of improper cleaning and brushing habits. Periodontal disease has four phases, without one of them being preventable. It impacts not just the gums but also the jawbone, causing dental problems as well as other systemic problems.
Periodontitis is likely to experience that may be avoided in most cases. Brushing your teeth and gums a day, cleaning daily, and seeing your dentist will considerably enhance your odds of success. They treat periodontitis and lower your risk of acquiring it. Poor oral hygiene is frequently the cause.
What happens if You Have Periodontal Disease?

Your gums get irritated as a result of periodontitis. They may expand, bleed, and turn red because the disease is so intense, air pockets from among your teeth and gums.
Bacteria can enter and grow in these spaces, causing illness beneath the gum line. The infection is then combated by your immune response. It gradually dissolves the tissue and organs that hold teeth in place. This reaction might result in tooth loss.
Different Stages of Periodontal Disease:

Gingivitis, mild periodontal disease, moderate periodontitis, and severe dental problems are the four phases of periodontal disease.
Gingivitis:
Gum disease is divided into two types: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gums that the blood when flossing, chronic poor breath, and gums. They seem inflammatory or considerably darker than usually are all signs of periodontitis. Therefore, periodontitis is a severe type of gum disease that commonly develops if gingivitis is left untreated.
Periodontitis:
Your gums will suffer the same indications as gingivitis, as well as a few additional ones, in a much more advanced stage of periodontitis. Periodontitis is typically painless before it is quite severe.
But when our teeth loosen, it really can cause discomfort. Untreated periodontal will ultimately occur in tooth loss. Deep enough pockets in his gums that accumulate food debris receded gums, pus among your teeth. Therefore, differences in the way your bite fits properly are all signs of periodontitis.
Moderate Periodontal Disease
The third stage of periodontitis, like mild periodontal disease, can be restored. Cleaning and root planning are thorough cleaning procedure that removes bacterial deposits that have been fixed in your gums. Therefore, the same signs as two stages appear at three stages.
But probe depths are larger at six to seven millimetres, allowing more germs to assault, not just your bones. But they are circulation and people with health problems. These phases can lead to bone and tooth loss, gum discomfort, increasing bleeding, and tooth movement if left untreated. Therefore, learning and root planning are used to treat periodontitis in stages two and three.
Advanced Periodontal Disease
When periodontal disease progresses to its ultimate stage, the infections penetrate even more, and the bacterium transforms into disorder bacterial once more. You now have a 50% – 90% chance of losing bone mass.
To release the deep disease pockets that already have developed, periodontal surgeries or periodontics laser treatment is required. If left untreated, phase four periodontics disease causes tooth separation or gaps, gum retraction.
They need dentures and some other major health issues. However, extensive periodontal disease involves red, inflamed, pus-filled gums, cold hypersensitivity, increased tooth displacement, painful chewing, and significant gum disease, in addition to bone loss.
Who is at the Risk of Periodontal Disease?

Periodontitis is also much more common in men. One factor might be that males are much less likely to visit the dentist on a routine basis. They also have poorer dental care.
Some variables that might make you more vulnerable to periodontitis include:
- Diabetes, considering persons with diabetes are more likely to have diseases.
- Cancer and AIDS are examples of diseases that impair the immune system’s ability. One of the most severe forms of periodontal is process and system periodontics, which is caused by certain disorders.
- Medications that reduce saliva production, which preserves your gums. Decongestants, psychologists, and hypertensive medications are among these treatments (high blood pressure).
- Genetics – you may be predisposed to certain diseases due to your genes.
- Smoking (the most important factor) reduces the body’s strength to fight illness.
- Hormonal issues in women are associated with pregnancy or the use of birth control pills.
What are the Potential Causes of Periodontal Disease?

Plaque, a sticky covering made of bacteria, is the most common cause of periodontitis. That is how bacteria can progress to periodontitis if left untreated:
Plaque can cause gingivitis:
Periodontitis, the mildest type of gum disease, is caused by plaque. Gum disease is an infection and swelling of the gum tissue surrounding your teeth’s bases (gingiva). Gingivitis can be treated and corrected with expert help and basic dental hygiene at home.
Plaque forms on your teeth:
Whenever food is carbohydrates and sugars mix with microorganisms located in your mouth. Plaque is removed by brushing twice per day and cleaning once every day. However, plaque returns fast.
Plaque can harden under your calculus:
If plaque remains between your teeth, it might solidify beneath your plaque. Tartar is much harder to get clear of and contains microorganisms. Tartar cannot be removed by brushing teeth alone; it requires highly skilled dental treatment. Bacteria and tartar cause greater harm the longer they stay on your teeth.
Gum inflammation:
Inflammation between your gums is ultimately filled with plaque, tartar, and germs. These pockets deepen with time, accumulating more germs. In addition, the long-term inflammatory response might tax your immune response. Most deep diseases affect tissue and bones desorption. You might just lose one or more teeth if they are not managed.
Bacteria in the mouth affect the tissue that surrounds the tooth, producing inflammatory and periodontal disease. However, tartar can extend beyond the gum line, making teeth more difficult to clean. Even just a dental health specialist could then clean the tartar and put an end to the periodontitis. When germs remain on the teeth for an extended period, they produce a film called plaque, which turns into tartar, also known as calculus.
How Can Dental Clinic Expert Diagnose Periodontitis?

During a normal dental checkup at Dental Clinic, dentists would be able to spot early indications of periodontal. That’s why it’s critical to have your teeth checked by a dental on a routine basis. They can keep track of your periodontitis over time to ensure it doesn’t deteriorate.
To evaluate any pockets on your gums, your dentists would use probing, which is a little ruler. They could also examine dental X-rays or send you to a periodontal, which specializes in diagnosing and treating and treatments of periodontitis. Typically, this exam is painless. If plaques tartar, then both are detected on your teeth during deep cleaning, your dentists will remove them.
How Can You Treat Periodontal Disease?

Gum disease therapy aims to encourage the reattachment of strong gums to teeth, minimize swelling, pockets level, and infections risks, and prevent disease development. Gum Disease Treatments contains a detailed discussion of the different therapeutic choices.
The type of therapy you receive is determined by the phase of your condition. Therefore, non-surgical therapy to inhibit bacterial development is available, as well as surgery to replace supporting tissues whether they responded to previous therapies and your general health.
Periodontitis can be treated with a variety of non-surgical and surgical options. Specialists at the dental clinic will prescribe a treatment plan for you depending on your unique circumstances, such as the extent of your periodontal.
Cleaning and root planning at a Dental Clinic are two non-surgical procedures that are frequently combined. Therefore, scaling removes germs from both teeth and behind your gums. If your periodontitis is established, flap therapy or pocket removal surgery may well be a perfect idea. Doctors usually recommend antibiotics to prevent infection and guarantee that any dangerous germs underneath your gum line have already been eliminated.
You have non-surgical or surgical treatments. Doctors will create incisions in your gums during the procedure to treat the roots of your teeth very immediately and completely. At the same time, root planning softens the sides of your dentinal tubules to try and prevent further bacteria accumulation.
Suggested Treatment for Periodontal Disease:

Deep dental cleaning:
We eliminate all plaque and tartar up from the ground to your gum line throughout a basic dental cleaning. To prevent your periodontitis from progressing further. Therefore, we normally prescribe less frequent dental professional cleaning.
Scaling and Root Planning:
Scaling and root planning is a non-surgical, effective cleaning technique done using a local anaesthetic on the patient’s teeth. We soften the tooth root even during the preparation phase to help eliminate infections and provide a smooth surface, therefore, for gums to repair the teeth. We scratch away all tartar and plaque throughout this therapy.
Flap Surgery/Pocket Reduction Surgery:
Surgery is required for more advanced symptoms of periodontal disease. The gums are pulled back before flap surgery so that we may properly remove any tartar. The gums are then securely fitted to the teeth, reducing the gap between both the gum and the tooth.
Bone Grafts:
Bone grafts are required when bones loss has occurred. To restore damaged jawbone caused by periodontal disease, our periodontics experts might utilize portions of your bones or a synthesized bone.
Recovery Tips for Periodontal Disease:

Your recovery will be determined by your general health, the severity of your periodontitis, and the therapy you get. Any operation will result in some bleeding, pain, and discomfort. It really should, therefore, clear up in a few days.
During periodontal disease, Dental Clinic advise you to stop smoking since it might impact how your system heals. Following your operation, we may recommend a specific mouth rinse or antibiotics. Please make good use of them for the means effective. After gum-treating diseases, we prescribe a soft-based diet for at least two weeks.
Are Dental Implants Better for the Recovery of Periodontal Disease?
Yes, for your teeth and general health, dental work is the greatest dental implant choice. But this is what they do below the gum line that makes them the greatest choice. In reality, the titanium metal helps the bones to expand around that one.
They keep it much more securely in position, reducing small bone losses in your jaw. Sure, they provide greater stability than some other treatment methods, and you feel like you’re getting your tooth structure restored. Dental Clinic works to activate the bones in your jaws in the same manner as the remaining tooth roots do, preventing bone loss.
Final Verdict:
Despite this, they are conducting appropriate dental hygiene and maintaining various healthy lifestyle changes. However, you have a higher risk of gum disease. Your dentists or periodontics specialist may prescribe less regular examinations, regular cleaning, and therapies to help you control the disease.
The American Academy of Periodontology estimates that at least 30% of Americans are genetically disposed to gum disease. If someone in your family has dental problems, you may be at a higher risk. Those that are genetically prone to periodontitis may well be more to significantly more likely to get it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the best way to treat periodontal disease?
- Surgical on the flaps (pocket reduction surgery). Your periodontics will make small incisions in his gums to remove a piece of gum tissue away from the roots. They result in more efficient cleaning and root planning.
- Bone grafting
- Soft tissue grafts
- Organ regeneration under guiding.
What are the four phases of gum disease?
Gingivitis, severe periodontal disease, significant dental problems, and severe periodontitis are the four phases of periodontitis.
What happens if you don’t cure periodontal disease?
Gum disease is a gum disease that is brought on by poor dental hygiene. Periodontitis arises when plaque builds strong bones and teeth and hardens. If left untreated, this can cause damage to the jaw and possibly tooth loss.
Is it possible for a dentist to treat periodontal disease?
Fortunately, restorative dental techniques such as pockets reduction surgery gum implants treat gum regression. However, bone plates to repair lower jaw decline may help restore a lot of these damages.
Is periodontitis a dangerous condition?
Periodontitis is a dangerous gum disease that can result in the loss of teeth as well as other major health issues. Periodontitis is a dangerous gum infection that causes muscle tissue. They can harm the bones that support your teeth if left untreated.
